Technology
Google’s Founding Story And How It Became What It Is Today

Search engines and web domains have been around since the beginning of the internet. Despite being the most popular search engine now, Google has been around for a very short period of time. Here is how this search engine conglomerate was founded!
The beginning
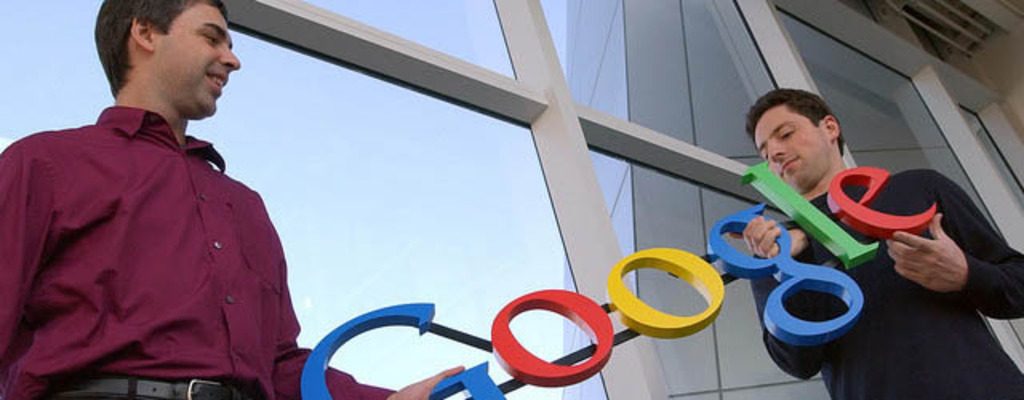

Like all love stories, Larry Page’s and Sergey Brin’s story had very troubled beginnings. The two met for the first time at Stanford University in the year 1995 and from the moment they locked eyes, everyone around knew trouble would follow. At the time, Brin was a second year student, whose job was to take potential students around campus and Page, an interested student, ended up in Brin’s group.
Walking up and down the hill, Brin and Page could not stop arguing with each other, constantly debating and fighting over everything from the weather to the historic places of San Francisco. Obnoxious, social and extremely opinionated, Page and Brin were poles apart in every way. What made them come together then? Their interests and desire to create a one of a kind search engine.
The first project

Page and Brin were thrown together for the first time ever when they started writing the code for a search engine, then called BackRub, because of its ability to analyse backlinks. Despite the tumultuous relationship shared by the co writers, the code became a massive success. So successful was the project that it resulted in the creation of a research paper titled The Anatomy of a Large Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine.
BackRub was unique in its functionality. By using an internally developed technology called PageRank, BackRub ranked a website’s importance by taking into account the number of pages on the website, the importance of the pages and the number of times they were linked to to the original site. The product was relatively successful but unfortunately, buyers were not interested in getting a product which was still in its initial stages. Finally, after multiple rejections. Brin and Page decided to innovate and create something new with (hold your breaths) Google!
The name that changed the world

Page and Brin took inspiration for the name Google from Gogol and voila, the strategy worked! A new name and a new beginning was all the founders needed for Google to get the much needed investors. Sun Microsystems co founder Andy Bechtolsheim was so impressed that after a quick demo of Google, he told the pair “Instead of us discussing all the details, why don’t I just write you a check?”
Bechtolsheim’s check was for $ 100,000 (made out to Google Inc) giving Page and Brin the much needed push toward success. The first two weeks after the founders got the check was quite an iconic one. With more than enough money in the bank, the duo opened their first office in Menlo Park, California. Post that, Google.com, a search engine that answered more than 10,000 questions a day, was launched.
History was created
Four years later, Page and Brin dropped the word beta from Google’s title and in 2001, Google finally filed and received a patent for its Ranking Technology! After that, there was no stopping Google and ever since, the search engine has changed the way the internet works. Interestingly, the first ever Google Doodle of the Burning Man was created to talk about the company’s motto, “Do No Evil.”
Google has come a long way, from being an accidental company to being one of the largest in the world. With exquisite patents to its name and extensive research at its hands, Google has definitely created a place for itself in the world of technology and innovation.
Artificial Intelligence
UAE G42 Launches 8-Exaflop AI Supercomputer in India for Sovereign AI 2026

UAE-based G42 has announced plans to deploy an 8 exaflop AI supercomputer in India, announced at the AI Impact Summit 2026 in Delhi. This national-scale project partners with Cerebras, MBZUAI, and India’s C-DAC, operating under full Indian data sovereignty as part of the India AI Mission.
The supercomputer boosts sovereign AI capabilities, enabling startups, researchers, academics, SMEs, and government access for tailored applications like public services and language tech. G42 India CEO Manu Jain highlighted its role in making India AI-native while prioritizing security.
This follows India-UAE tech pacts in late 2025, positioning India among global leaders in exaflop AI infrastructure amid rising demand for localized compute. Cerebras CSO Andy Hock noted it will accelerate large model training for India-specific needs.
News
Google Launches Startup Hub in Hyderabad to Boost India’s Innovation Ecosystem

Google has launched the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad, a major step in strengthening India’s dynamic startup ecosystem. This new initiative aims to empower entrepreneurs, innovators, and developers by giving them access to Google’s global expertise, mentoring programs, and advanced cloud technology. The hub reflects Google’s mission to fuel India’s digital transformation and promote innovation through the Google for Startups program.
Located in the heart of one of India’s top tech cities, the Google Startup Hub in Hyderabad will host mentorship sessions, training workshops, and networking events designed for early-stage startups. Founders will receive Google Cloud credits, expert guidance in AI, product development, and business scaling, and opportunities to collaborate with Google’s global mentors and investors. This ecosystem aims to help Indian startups grow faster and compete globally.
With Hyderabad already home to tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, the launch of the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad further cements the city’s position as a leading innovation and technology hub in India. Backed by a strong talent pool and robust infrastructure, this hub is set to become a growth engine for next-generation startups, driving innovation from India to global markets.
Technology
Jio Unveils Cloud PC Service to Bring Affordable Computing to Indian Households

- Jio Platforms has launched JioPC, a cloud-based virtual desktop service that transforms any television connected to a Jio Set Top Box into a fully functional computer.
- Users simply connect a keyboard and mouse to access a desktop-like environment, complete with web browsing, productivity tools, and educational apps—all without needing a physical PC or extra hardware.
- The service is device-agnostic and works with all consumer PC brands, making advanced computing accessible and affordable for millions across India.
JioPC is designed to support a wide range of activities, from professional work to online learning and creative projects. By leveraging Jio’s robust cloud infrastructure, users can run even compute-intensive AI applications directly from their TV screens. The platform also ensures data security and reliability, as all files and settings are safely stored in the cloud, protecting users from data loss even if their device is reset or replaced.
With JioPC, Jio aims to democratize digital access and bring high-performance computing to Indian households at a fraction of the traditional cost. The service supports popular productivity suites like LibreOffice and Microsoft Office online, and Jio is offering a free trial to encourage users to experience the benefits firsthand. This innovative move is set to reshape how people in India work, learn, and connect in the digital age.













GO88
November 5, 2025 at 1:24 pm
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
MM88
November 7, 2025 at 3:26 am
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
站群程序
November 9, 2025 at 5:10 pm
搭载智能站群程序,自动化搭建与管理,为SEO项目提供核心驱动力。站群程序
J88
November 10, 2025 at 12:40 am
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
iwin
November 19, 2025 at 11:21 am
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
Kuwin
November 21, 2025 at 12:00 am
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Kings Casino Freispiele anmelden
December 21, 2025 at 4:45 am
Daher haben wir natürlich auch die mobile Verfügbarkeit
des Powbet Casinos ganz genau unter die Lupe genommen. Nicht mehr wird
der meiste Umsatz über den PC platziert, viel mehr sind mobile Online Casinos immer populärer geworden. Dort
könnt ihr bis zu 200 Euro auf eure Verluste beim Blackjack, Roulette
oder Baccarat zurückerhalten.
Die Plattform bietet eine breite Palette an modernen Zahlungsmöglichkeiten für Ein- und Auszahlungen. Die Zahlungsabwicklung erfolgt bei
Powbet sicher, schnell und unkompliziert. Der Live-Bereich bietet authentisches
Casino-Flair mit professionellen Dealern.
Der Willkommensbonus wird automatisch bei Ihrer ersten Einzahlung gutgeschrieben. Über 15 sichere Zahlungsmethoden für maximale Flexibilität Ihr 100% Bonus bis €500 +
200 Freispiele werden automatisch Ihrem Konto gutgeschrieben.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/beste-online-casinos-2025-empfehlungs-guide/