Technology
Unbelievable: A Whole House Made Within 24 Hrs Using 3-D Printing, Watch Video
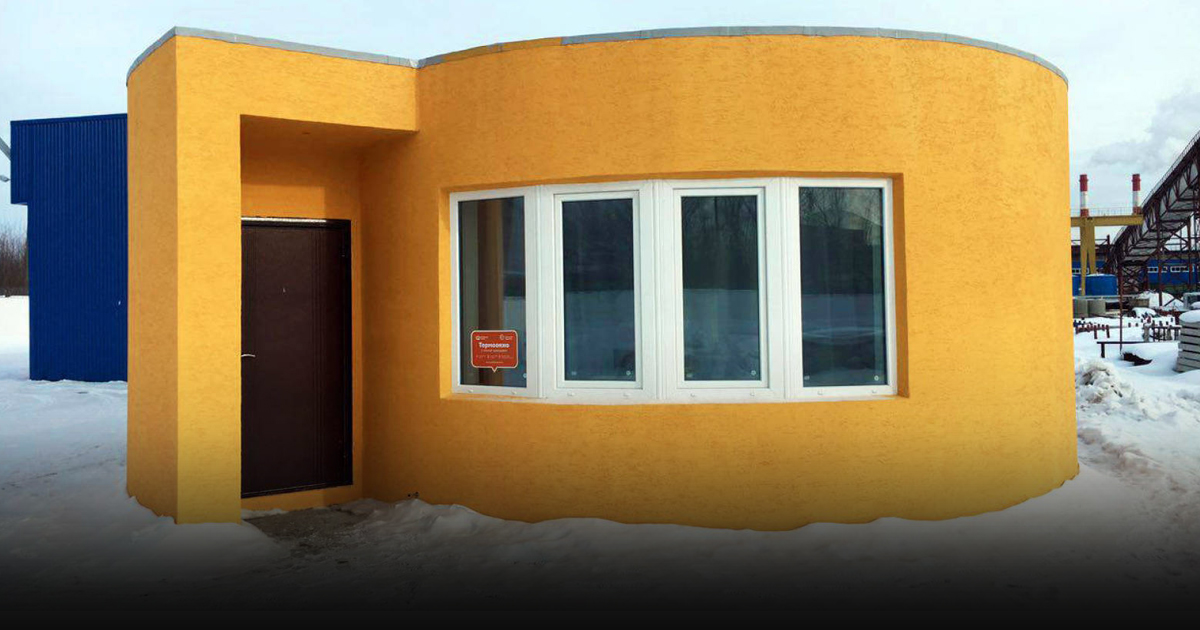

It is not a toy house we are talking about. This is a residential house which was built using an advanced technology 3 D printer. San Francisco-based startup Apis Cor built a house in a Russian town within 24 hours with the help of 3 D printing.
These printers are huge and bulky. The walls of the house were printed entirely on site. This is the world’s first ever actually printed house. The innovative design makes it happen actually.
Watch the video here:
This consisted of a noble 3 D printer and an automatic mix and supply unit which is combined to make the construction printing process as much automated as possible. The equipment is unique and has no analogs in the world till date.
This printer has unique features such as high printing speed, ease of transport and is lightweight and compact. This equipment has a commendable feature of operating in any temperature including the hottest summers, the coldest winters or as in temperature of -35 degrees.
From inside, these printed houses are no different from the regular concrete houses, these printed houses are as comfortable and reliable as man-made houses. This world’s first ever printed house is about 38 square meter and the cost of building this is about $ 275 per square meter. This amount includes all work and material costs.
Artificial Intelligence
UAE G42 Launches 8-Exaflop AI Supercomputer in India for Sovereign AI 2026

UAE-based G42 has announced plans to deploy an 8 exaflop AI supercomputer in India, announced at the AI Impact Summit 2026 in Delhi. This national-scale project partners with Cerebras, MBZUAI, and India’s C-DAC, operating under full Indian data sovereignty as part of the India AI Mission.
The supercomputer boosts sovereign AI capabilities, enabling startups, researchers, academics, SMEs, and government access for tailored applications like public services and language tech. G42 India CEO Manu Jain highlighted its role in making India AI-native while prioritizing security.
This follows India-UAE tech pacts in late 2025, positioning India among global leaders in exaflop AI infrastructure amid rising demand for localized compute. Cerebras CSO Andy Hock noted it will accelerate large model training for India-specific needs.
News
Google Launches Startup Hub in Hyderabad to Boost India’s Innovation Ecosystem

Google has launched the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad, a major step in strengthening India’s dynamic startup ecosystem. This new initiative aims to empower entrepreneurs, innovators, and developers by giving them access to Google’s global expertise, mentoring programs, and advanced cloud technology. The hub reflects Google’s mission to fuel India’s digital transformation and promote innovation through the Google for Startups program.
Located in the heart of one of India’s top tech cities, the Google Startup Hub in Hyderabad will host mentorship sessions, training workshops, and networking events designed for early-stage startups. Founders will receive Google Cloud credits, expert guidance in AI, product development, and business scaling, and opportunities to collaborate with Google’s global mentors and investors. This ecosystem aims to help Indian startups grow faster and compete globally.
With Hyderabad already home to tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, the launch of the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad further cements the city’s position as a leading innovation and technology hub in India. Backed by a strong talent pool and robust infrastructure, this hub is set to become a growth engine for next-generation startups, driving innovation from India to global markets.
Technology
Jio Unveils Cloud PC Service to Bring Affordable Computing to Indian Households

- Jio Platforms has launched JioPC, a cloud-based virtual desktop service that transforms any television connected to a Jio Set Top Box into a fully functional computer.
- Users simply connect a keyboard and mouse to access a desktop-like environment, complete with web browsing, productivity tools, and educational apps—all without needing a physical PC or extra hardware.
- The service is device-agnostic and works with all consumer PC brands, making advanced computing accessible and affordable for millions across India.
JioPC is designed to support a wide range of activities, from professional work to online learning and creative projects. By leveraging Jio’s robust cloud infrastructure, users can run even compute-intensive AI applications directly from their TV screens. The platform also ensures data security and reliability, as all files and settings are safely stored in the cloud, protecting users from data loss even if their device is reset or replaced.
With JioPC, Jio aims to democratize digital access and bring high-performance computing to Indian households at a fraction of the traditional cost. The service supports popular productivity suites like LibreOffice and Microsoft Office online, and Jio is offering a free trial to encourage users to experience the benefits firsthand. This innovative move is set to reshape how people in India work, learn, and connect in the digital age.












Vmysbrfd
May 27, 2025 at 5:49 am
Explore the ranked best online casinos of 2025. Compare bonuses, game selections, and trustworthiness of top platforms for secure and rewarding gameplaycrypto casino.
Metis.lti.cs.Cmu.edu
May 29, 2025 at 11:33 pm
Lastly, the chopping part is actually a low-carb weight loss
plan, with suggestions to cut 500 to 1,000 calories from the upkeep section. This part should be run until you achieve a desired physique fats proportion, ideally less than 10 %.
The maintenance/induction section is suggested for weeks one to four with caloric
consumption levels of 18 times your body weight in pounds.
With this record of meals which are like natural steroids, you’re nicely on your way to success.
Avocados are a wholesome supply of fat but when eaten in extra they can increase calorie intake
and stop muscle progress. Beef is a good source for bodybuilders trying to enhance their testosterone
ranges, promote muscle achieve, and cut back muscle soreness.
If persons are interested in natural steroid dietary supplements, the most secure choice is to seek the advice of with a doctor before taking any dietary dietary supplements.
As a versatile vegetable, avocados could be incorporated into salads, smoothies, and other meals to offer lasting benefits when building muscle.
If an individual is excited about taking supplements to aid their
exercises, they should first speak with a well being care provider to examine the product is secure for them.
Unfortunately, licorice root can elevate the blood pressure (just like Prednisone) in sure prone people.
So, this will not be the best choice for so much of who suffer from persistent irritation. On the opposite hand, licorice could be a fantastic profit to those affected by
low vitality brought on by low blood pressure (hypotension).
An effective anti-inflammatory dose of curcumin for many conditions is
mg, three times every day with food. Military Muscle is probably
certainly one of the best and most reliable dietary supplements to spice up testosterone.
Military Muscle is a combination of fourteen pure elements which can boost testosterone
levels. These anabolic steroids have dangerous side effects, together with
blood clots and prostate most cancers; it’s subsequently clever to consult a
medical supplier prior to beginning use of anabolic steroids.
Nevertheless, since true natural bodybuilding would
by no means attract as a lot consideration as the unnatural variations,
the sponsors enable using steroids in pure showsand encourage their participation.
Cortisol ranges are essential to a number of elements of
well being and wellbeing, and your healthcare provider can measure them via
blood, saliva, or urine tests. This might end in symptoms like weight gain or loss,
high blood pressure and elevated or decreased sugar ranges.
Estrogens are produced by the ovaries (an organ that holds immature eggs).
Ovary tissues additionally produce and secrete different steroid hormones like
prolactin and luteinizing hormone; together these hormones regulate ovulation and menstruation. Steroid hormone biosynthesis is tightly managed by tropic hormones in the adrenal gland and gonads, whereas additionally requiring an plentiful supply of cholesterol substrate for manufacturing.
SCP2 performs a vital role in transporting cholesteryl
esters from plasma and HDL lipoproteins into mitochondria for use in steroidogenesis, offering speedy responses to trophic hormones.
A cis/trans or trans/cis configuration is crucial for binding of steroid hormones
to their receptors, so as to act as hormones.
Ecdysteroids are the steroid hormones of arthropods, the place they regulate moulting, metamorphosis,
replica and diapause (Koolman 1989). Ecdysteroids are a kind of steroid hormone present
in insects, sure water animals, and some crops. Ecdysteroids have an identical structure to the male hormone testosterone, however
there’s no evidence that it works like testosterone in humans.
Studies have discovered Ecdysterone to increase anabolism with out affecting androgens like testosterone.
Huge Vitamin is utilizing the pure form of ecdysteroids, which is
simply pure Ecdysterone and 20-hydroxyecdysone. I Take a tablespoon of pure olive oil (ordered from Italy), both directly before, typically after,
I take my Turmeric. While i recognize the effort
and wealth of information that went into this text, there is a big gap
in it. Sure, both black pepper and ginger do make it extra biologically obtainable as
soon as it passes into your blood stream, but without fat, it
won’t be absorbed into the blood stream and may have a really restricted effect.
A sweetener like honey or maple and lemon wedge are elective elements
to enhance its taste profile. If you want a great immune modulator,
here is a fast and simple recipe you’ll find a way to whip at house.
This not only provides a wealthy source of protein and healthy fat but additionally adds a selection of vitamins and minerals, making
it a superb post-workout snack to reinforce restoration. Exploring totally different recipes and meal combos can hold your food plan each exciting and healthful.
Whereas natural steroid foods can considerably
help muscle building and overall well being, relying solely
on them may not be sufficient. Muscle growth is a complex
process that requires a mixture of correct vitamin, power coaching,
and restoration. Including a selection of nutrient-dense foods in your food regimen is important for ensuring you
get all the required vitamins and minerals
wanted for optimum muscle perform and progress. Beans
include pure anabolic steroids referred to as saponins that are identified to stimulate
testosterone manufacturing and decrease cortisol ranges, both key components of muscle
progress. One of the best methods to extend your consumption of plant-based geneza
steroids for sale (Metis.lti.cs.Cmu.edu) is thru your diet.
There is not any one-size-fits-all reply within the pure versus artificial steroids debate.
It in the end comes down to individual aims and contemplating the
potential health effects. While artificial steroids may provide fast positive aspects, they carry significant risks.
On the other hand, pure steroids provide a safer and extra
sustainable method to hormone balance and general well-being.
Prioritising hormone steadiness and exploring
steroid alternatives can enhance long-term health outcomes.
It’s advisable to hunt steerage from a healthcare professional earlier than initiating hormone-related measures
to guarantee well-informed decisions and secure practices throughout your fitness journey.
In conclusion, whereas synthetic steroids may present more
instant and potent results on muscle development and energy, plant-based steroids provide a safer and extra holistic
strategy.
It is very effective in offering immune help and protection to hurry up therapeutic.
Echinacea is very potent and should not be used
with other drugs together with prednisone. Although prednisone is a vital drug that’s efficient for several conditions,
it’s necessary to know what to eat when you’re taking it.
Your physician could ask you to follow a low-salt, high-potassium, or
high-calcium diet.
Nordichardware.se
June 4, 2025 at 4:47 pm
No, Anabolic steroids are considered managed substances in the USA,
and without prescription use, their consumption is outlawed.
Every case of possession and distribution of anabolic steroids without
an applicable prescription is punishable. A long-acting type of testosterone that is extensively used
for bulking cycles.
In different words, assuming that the pre-steroid era bodybuilders of the ’40s
and early ’50s represented the absolute peak of drug-free muscular development is extremely naive.
Bodybuilding’s athlete pool was actually extra limited than that of Olympic
sports. Calling bodybuilding an underground sport within the ’40s and ’50s can be an understatement.
Before we dive into the relationship between Best steroids to get big Fast (Nordichardware.se)
and weight loss, it’s essential to know what
steroids are and the way they function within the body.
Steroids, also known as anabolic-androgenic steroids, are artificial variations of the male hormone testosterone.
These substances are designed to mimic the consequences of testosterone, promoting muscle progress, energy, and enhanced athletic performance.
Additionally, prednisone could cause weight achieve in canines, which can be a
contributing issue to the development of diabetes.
Merchandise that are pure, top-quality alternatives can now be included in diets by visiting Crazy Bulk and D-Bal Max
websites. One can acquire a superb amount of muscle mass and energy without any unwanted effects.
Anabolic steroids are used to grow extra muscle and improve athletic efficiency;
corticosteroids are used in lowering inflammation and treating medical circumstances like bronchial asthma and arthritis.
In truth, the working procedures of anabolic steroids and corticosteroids are quite totally different.
Besides their antagonistic results on these receptors, they possess various pharmacologic interactions with a
variety of neurotransmitter receptors (44).
The magnitude of weight achieve throughout antidepressant remedy differs considerably by class.
Observe how the woman above didn’t really lose
any weight (+2 kg), but she skilled dramatic fat loss.
Thus, as a end result of Anavar’s low toxicity, we find that customers generally do not experience any obvious unwanted effects when taking this
compound. Nevertheless, if abused with extreme dosages or overextended cycles, dangerous unwanted effects can happen. As Quickly As your testosterone base is in place, the subsequent step is selecting which compounds
to pair primarily based in your goal.
However, by reducing water weight via the reduction of estrogen, we often see HDL ldl cholesterol drop additional,
elevating blood strain. The most popular types of testosterone
used by our sufferers are cypionate and enanthate, as a end result of their longer ester structure
and ease of injections (causing minimal discomfort or pain).
Injections are only required a couple of times per week with these two esters, producing
slow and regular positive aspects. Based on our testing, testosterone
is the most secure anabolic from a cardiac perspective, only inflicting gentle adjustments in cholesterol and blood lipids.
Nevertheless, testosterone additionally has fat-burning effects (due to its high level of androgenicity), causing a reduction in adipose tissue.
Their work on enviroliteracy.org underscores the importance of being conscious of the potential impression of pharmaceutical
choices. Anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) are lab-made testosterone dietary supplements.
They’re by no means a good choice for building muscles
or power because of their numerous adverse side effects.
DMAA has been found in quite a few muscle-building and weight reduction dietary supplements,
however it’s not protected.
Thus, regardless of testosterone’s powerful anabolic nature, it may additionally be used as a cutting steroid.
Dianabol has a significant negative impact on ldl cholesterol and blood pressure, primarily based on our patient’s blood work.
This is as a end result of of Dianabol being an oral compound that causes water retention.
Dexamethasone is usually preferred when a long-acting, high-potency corticosteroid is required.
It is usually used in conditions similar to cerebral edema, severe allergic reactions, and
sure kinds of most cancers treatment. Its longer half-life and excessive potency provide
sustained and powerful anti-inflammatory results. This drugs may trigger thinning of the bones (osteoporosis) or sluggish growth in children if used
for a protracted time.
Consuming loads of water might help with fluid retention and overall well being.
Regular train may help fight weight gain, improve bone density, and boost your temper.
There are several intermittent fasting strategies that contain completely different home windows of time the place you eat and avoid consuming.
J88
November 7, 2025 at 8:25 am
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
ios超级签
November 8, 2025 at 11:33 am
苹果签名,苹果超级签平台,ios超级签平台ios超级签苹果企业签,苹果超级签,稳定超级签名
MM88
November 11, 2025 at 4:05 am
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
站群程序
November 12, 2025 at 7:22 pm
采用高效谷歌站群策略,快速提升网站在搜索引擎中的可见性与权重。谷歌站群
iwin
November 13, 2025 at 6:20 am
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
MM88
November 16, 2025 at 9:13 am
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Kuwin
November 16, 2025 at 11:13 pm
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
GO88
November 26, 2025 at 1:42 am
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
jili slot free 100
December 19, 2025 at 4:21 am
jili slot free 100 jili slot free 100
Monro Casino Cashback
December 21, 2025 at 7:39 pm
Dieses Willkommenspaket beginnt mit einem 120%-Bonus bis zu €240 plus 100
Freispiele auf „Enchanted Forest Of Fortune“ von Betsoft.
Verwende den Bonuscode SPINS20 nach der Registrierung, um dieses Angebot zu aktivieren. Registriere dich
über unseren exklusiven Link und gib unseren exklusiven Bonuscode ohne Einzahlung im Feld „Promo-Code“ auf der Registrierungsseite ein. Melden Sie sich noch
heute im Snatch Casino an und sichern Sie sich ein 450%-Bonuspaket
sowie 325 Freispiele für Ihre ersten Einzahlungen.
Selbst, wenn du viele Vollbilder an den Automatenspielen getroffen hast oder in der
Freispielrunde gespielt und 1.000 Euro gewonnen hättest.
Auch bei einem neuen Casino Bonus ohne Einzahlung gibt es
ein paar Punkte, die bei der Aktivierung und den darauf folgenden Freispielen beachtet werden müssen. Denk auch immer
daran, dich für den Newsletter deines Lieblingscasinos anzumelden. Wenn wir über ein Online Casino mit Echtgeld Bonus ohne Einzahlung sprechen,
ist das das klassische Gegenteil eines Einzahlungsbonus.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/leon-casino-auszahlung-der-umfassende-leitfaden-fur-reibungslose-gewinnauszahlungen/
**how do casino VIP programs work**
December 26, 2025 at 11:53 pm
These fit lessons, exams, rules, and study goals.
Matching strength to the situation keeps your meaning natural.
These show importance because the matter is serious, risky, or time sensitive.
These show importance because something has strong meaning or effect.
Synonyms for important help you explain value and priority in a clearer way.
Learn a new word every day. Comprehensive resource for word definitions and usage
Important means something matters for a reason, like influence or impact.
Use urgent when time is the main reason it matters. Important means something matters,
but urgent means it needs attention right now. These fit leaders, respected people, or key jobs.
Below is a list of common synonyms for important with short meanings.
In writing, a synonym can make your meaning sharper, like showing urgency,
greatness, or deep value.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/ax99-casino-australian-real-money-gaming-hub/
online gambling australia pokies
December 27, 2025 at 5:26 pm
Ready to roll the dice with the National Casino account?
Let’s guide you through the seamless process of starting your journey at this premier gaming destination. National Casino understands the importance
of reliable and accessible customer support.
National Casino’s commitment to player safety and fair
play is evident in its licensing and regulatory compliance.
If you’re more into simplicity and easy gameplay, then go for
online pokies. You’ll enjoy reload offers and cashback bonuses.
Who doesn’t love getting a bonus when they
enter an online casino? This online casino is easy to use,
but if you have some problems, customer support
is always ready to help you. There is no need to download the
app for iOS or Android because all games are mobile-optimized, and the
graphics are amazing on small screens. Besides promotions for new members, National Casino has offers for regular
players.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/golden-crown-casino-australia-in-depth-review/
booyoung-elec.com
December 29, 2025 at 12:09 pm
online casino mit paypal einzahlung
References:
booyoung-elec.com