Technology
Lofty Dreams: How The Flying Taxi May Finally Realize Our Desire for the Flying Car
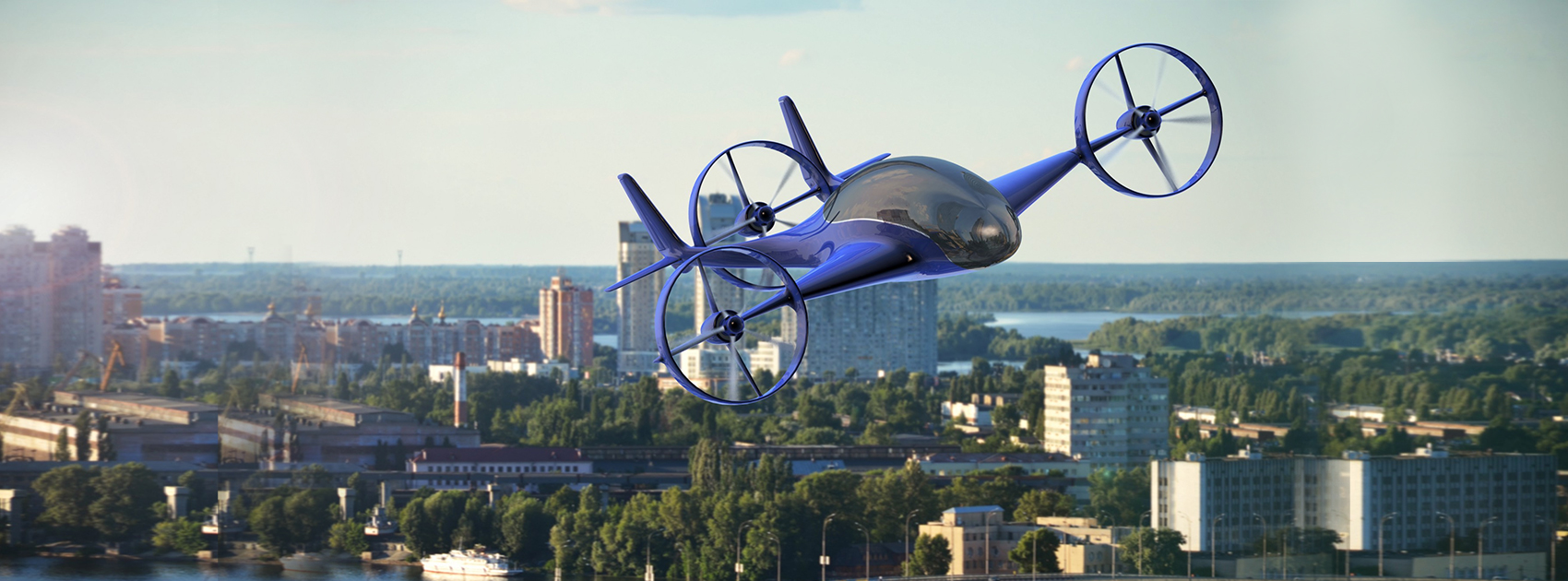

If you thought that the future of transportation was just electric cars and autonomous vehicles, well, there’s a push to take things a little higher.
Certainly, gasoline-free, self-driving cars are all the rage right now, and rightfully so. We are deep into the testing phase of cars that reach level four automation (level five means they are fully autonomous).
However, other transportation technologies are aiming to leave the road behind and take occupants above the fray of cars and traffic, delivering them to their destinations through the air versus across the ground.
While the promise of the flying car introduced in Back to the Future Part II may have missed the mark by a few years, the next decade will see a revolution unlike any since humans first took flight.
What is a Flying Taxi?
Traditionally, the term flying taxi is often confused with established transportation services known as Air Taxis. The latter evokes smallish airplanes or helicopters that shuttle occupants short distances, city to city, usually from one airport to another.
The modern iteration on a flying taxi, however, takes the terminology of a short-haul flight to a whole new level.
What makes the flying taxi concept both unique and potentially viable in a modern setting is the ability for the aircraft to take off and land anywhere – no airport is necessary.
Thanks to vertical ascent and descent capabilities the aircraft currently being tested are more akin to helicopters, but the design isn’t merely limited to well-known methods of flight. In fact, some prototypes now resemble oversized drones and gondola cabs with an array of small rotors attached to the roof.
Many of the designs carry only a handful of riders – from as few as two up to between five and seven, not including the pilot for the non-autonomous concepts. Indeed crewless flight is still one to two decades away, but much like the driverless automobile the drive for flying taxis to one day be pilotless is an aggressive one.
The small size though is the key to the technology proving a significant addition to an already crowded transportation network. So too is the plan for many of these crafts to be electric, eliminating the noise and nuisance of a gas powered engine.
In rising above gridlocked avenues and streets, flying taxis would utilize every aspect of the urban setting. From the ground level (in some areas) to the airspace in between or just above a cities mid and high rise buildings to the rooftops of those same structures, the tech would undoubtedly make the most of its operational field. Most proposals call for those rooftops to transition into launch and landing pads for the taxi network.
An actual airborne taxi service to get occupants from point A to point B within a densely packed city won’t just stop at the city limits though. There are also plans that would expand that reach, flying short haul, low occupant flights between closely networked cities.
Places within an hour’s drive of each other such as Dallas to Fort Worth or Baltimore to Washington DC are obvious candidates. However, taxi flights also offer the opportunity to bridge locales like Boston and New York or Los Angeles and San Francisco.
More Than Just Flying Cars

While on paper the whole enterprise seems ridiculously cool and simple enough, the reality is something different.
Uber, the peer to peer ridesharing behemoth, is one of the most visible players in the race to get the flying taxi up and running with its Elevate and UberAir programs.
In partnership with space agency NASA, Uber is working towards their taxis taking flight in 2020 in Dallas-Fort Worth, Los Angeles, and Dubai. It’s an aggressive goal considering that Uber remains in the design phase and have yet to produce an actual working, to scale prototype.
But they are undeterred.
Jeff Holden, head of product at Uber, has said, “there’s been a great deal of progress that’s been hard to see from the outside because a lot of this is just hard work at the drafting table.”
He goes on the to note, “we feel really good. It’s been a really interesting process getting our vehicle manufacturing partners aligned on performance specifications so that they’re building vehicles that align with what we need to make Elevate successful. So lots of good progress there.”
Expanding upon the ideas of their uncrewed traffic management protocols or UTM, NASA helps to nail down the infrastructure side of the endeavor.
The UTM system is currently helping to corral the unruly nature of the growing drone industry. In theory, NASA’s UTM would lead to the creation of an entirely new system of air traffic control to guide the taxi flights.
Although the push for localized flying transports has yet to generate the same publicity as that of their earthbound automobile counterparts, Uber is far from the only player in the field. More than 15 different companies are working towards similar goals, and in many cases, a lot of investment dollars are flowing into these efforts to get them off the ground.
For example, Kitty Hawk is a startup owned and fully funded by Larry Page, co-founder of Google. Kitty Hawk is currently testing a recreational hovercraft in New Zealand meant to dovetail into their flying taxi program over the next three years.
Others companies wanting to get in on the action include aviation heavyweights Boeing and Airbus.
Boeing bought Aurora Flight Service Corporation late last year to give both their commercial and military programs in electric and autonomous flight a shot in the arm. Greg Hyslop, the Chief Technology Office for Boeing noted the deal reflects that the “the aerospace industry is going to be changing” and Boeing is aiming to be ready “for whatever that future may be.”
For their part, Airbus made a similar deal, with an investment in startup Blade, which already boasts a charter flight business that is, ironically enough, often cast as the Uber of charters. This in addition to Airbus’ in-house Vahana program.
Elsewhere, showing off at CES 2018 in Las Vegas, was an 18 rotor vehicle called the Volocopter, that until recently was flying around in the futuristic desert playground of Dubai, running test flights.
Straight out of a sci-fi movie, the Volocopter is a German designed pilotless drone that one must really see to believe and appreciate.
Dubai also has a partnership with Chinese firm EHang, whose own ambitions for flying taxis stems from the automation and delivery via drone aircraft of organ transplant materials.
Even part and component manufacturers are playing a pivotal role in making the sci-fi of flying vehicles real.
British engine maker Rolls-Royce has a propulsion system in development for use in flying taxis. They hope to have it available sometime within the next decade.
And yes, some auto manufacturers are getting into the game with Porsche in the early stages of exploring the possibility.
Just How Viable Is A Flying Vehicle?
As with any new technology, growing pains exist. Flying cars are no different. There will almost certainly be a level of turbulence before the population fully embraces the latest tech and its scalable for the masses.
Consider the now ubiquitous iPhone is less than 12 years old and was once a curiosity. The prevalence and the advancements of the device made in just over a decade are definitely remarkable. The hope is that a flying taxi can follow a similar fast-track path to success.
Of course, airborne taxis are a completely different realm. As much as humanity is yearning to see a car fly – and practically – it’s another thing when you ask those same people to take a ride. It will require a convincing sales pitch for commuters to trust a machine that has onboard parachutes as part of its standard equipment.
However, with cities more crowded and street-level gridlock a constant complaint of urban dwellers, it’s not difficult to envision city skies filled with swarms of on-demand taxis.
The CEO of Volocopter, Florian Reuter summarizes the ease of use autonomous flight offers. “Implementation would see you using your smartphone, having an app, and ordering a volocopter to the next voloport near you. The volocopter would come and autonomously pick you up and take you to your destination,” he said.
Discounting that level of simplicity and convenience is hard.
As cool as it all sounds, flying taxis – even with actual testing happening as we speak – remain a construct of the future. We noted that many of the target dates for these aerial taxi programs run between 2020 and 2030. For some, those timelines are highly ambitious.
Even those whose entire reputation derives from their lofty ambitions.
Elon Musk mused to Bloomberg during a recent interview his thoughts on flying cars, and it was less than favorable. “Obviously, I like flying things. But it’s difficult to imagine the flying car becoming a scalable solution,” he said.
Uber’s Holden, however, disagrees. “We’ve studied this carefully and we believe it is scalable,” he noted, also casting Musk’s comments as “off the cuff” and “random.”
Final Thoughts
Regardless of if it can actually happen anytime within the next few years, many are banking on it simply being a matter of time before we are living with the daily sight of flying taxi services buzzing over our heads.
While the initial product may prove a bit different from the original vision, few will argue should one of the longest held fantasies of future progress finally come true.
Written by – Anna Kučírková
Artificial Intelligence
UAE G42 Launches 8-Exaflop AI Supercomputer in India for Sovereign AI 2026

UAE-based G42 has announced plans to deploy an 8 exaflop AI supercomputer in India, announced at the AI Impact Summit 2026 in Delhi. This national-scale project partners with Cerebras, MBZUAI, and India’s C-DAC, operating under full Indian data sovereignty as part of the India AI Mission.
The supercomputer boosts sovereign AI capabilities, enabling startups, researchers, academics, SMEs, and government access for tailored applications like public services and language tech. G42 India CEO Manu Jain highlighted its role in making India AI-native while prioritizing security.
This follows India-UAE tech pacts in late 2025, positioning India among global leaders in exaflop AI infrastructure amid rising demand for localized compute. Cerebras CSO Andy Hock noted it will accelerate large model training for India-specific needs.
News
Google Launches Startup Hub in Hyderabad to Boost India’s Innovation Ecosystem

Google has launched the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad, a major step in strengthening India’s dynamic startup ecosystem. This new initiative aims to empower entrepreneurs, innovators, and developers by giving them access to Google’s global expertise, mentoring programs, and advanced cloud technology. The hub reflects Google’s mission to fuel India’s digital transformation and promote innovation through the Google for Startups program.
Located in the heart of one of India’s top tech cities, the Google Startup Hub in Hyderabad will host mentorship sessions, training workshops, and networking events designed for early-stage startups. Founders will receive Google Cloud credits, expert guidance in AI, product development, and business scaling, and opportunities to collaborate with Google’s global mentors and investors. This ecosystem aims to help Indian startups grow faster and compete globally.
With Hyderabad already home to tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, the launch of the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad further cements the city’s position as a leading innovation and technology hub in India. Backed by a strong talent pool and robust infrastructure, this hub is set to become a growth engine for next-generation startups, driving innovation from India to global markets.
Technology
Jio Unveils Cloud PC Service to Bring Affordable Computing to Indian Households

- Jio Platforms has launched JioPC, a cloud-based virtual desktop service that transforms any television connected to a Jio Set Top Box into a fully functional computer.
- Users simply connect a keyboard and mouse to access a desktop-like environment, complete with web browsing, productivity tools, and educational apps—all without needing a physical PC or extra hardware.
- The service is device-agnostic and works with all consumer PC brands, making advanced computing accessible and affordable for millions across India.
JioPC is designed to support a wide range of activities, from professional work to online learning and creative projects. By leveraging Jio’s robust cloud infrastructure, users can run even compute-intensive AI applications directly from their TV screens. The platform also ensures data security and reliability, as all files and settings are safely stored in the cloud, protecting users from data loss even if their device is reset or replaced.
With JioPC, Jio aims to democratize digital access and bring high-performance computing to Indian households at a fraction of the traditional cost. The service supports popular productivity suites like LibreOffice and Microsoft Office online, and Jio is offering a free trial to encourage users to experience the benefits firsthand. This innovative move is set to reshape how people in India work, learn, and connect in the digital age.













Ieodqtyq
May 23, 2025 at 3:37 pm
Explore the ranked best online casinos of 2025. Compare bonuses, game selections, and trustworthiness of top platforms for secure and rewarding gameplayBonus offer.
Kuwin
November 5, 2025 at 8:14 pm
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
站群程序
November 7, 2025 at 1:46 am
搭载智能站群程序,自动化搭建与管理,为SEO项目提供核心驱动力。站群程序
GO88
November 7, 2025 at 12:40 pm
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
站群程序
November 9, 2025 at 4:44 pm
搭载智能站群程序,自动化搭建与管理,为SEO项目提供核心驱动力。站群程序
MM88
November 12, 2025 at 7:53 am
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
iwin
November 17, 2025 at 4:38 am
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
MM88
November 19, 2025 at 5:58 pm
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
J88
November 21, 2025 at 11:15 pm
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.