Technology
How Popular Websites Looked Like When They Were Launched
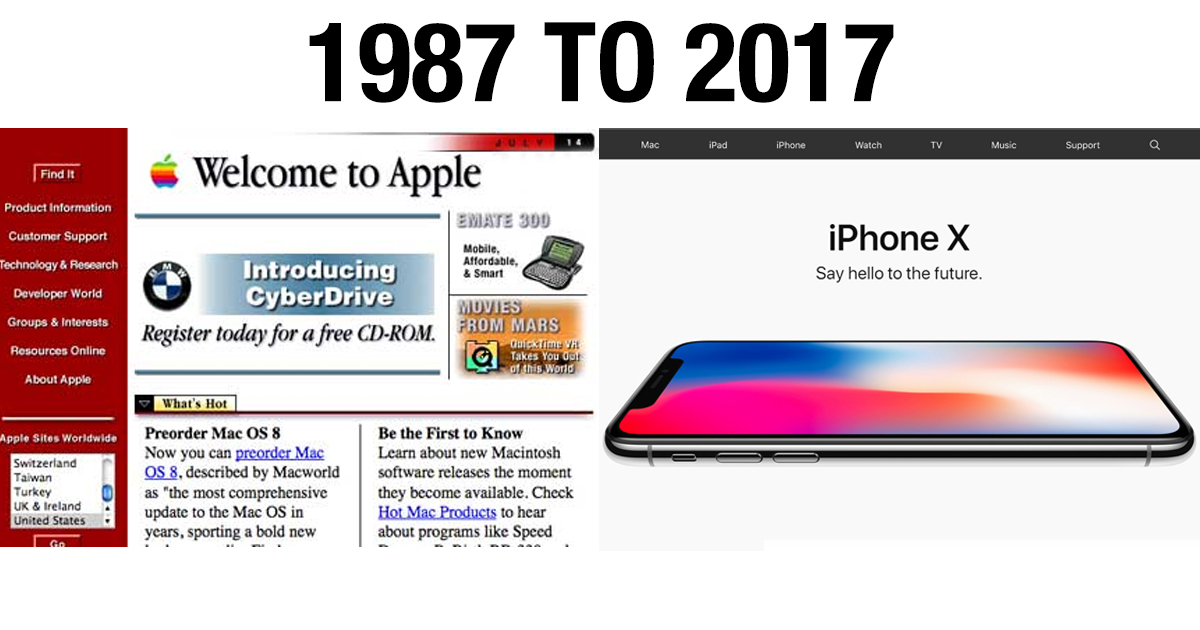
Before social media became synonymous with Facebook or Twitter and before Google became equivalent with research, the popular websites of today were not as advanced. Although the technology was not as advanced as it is today, this is how our beloved websites looked like, way back in the day.
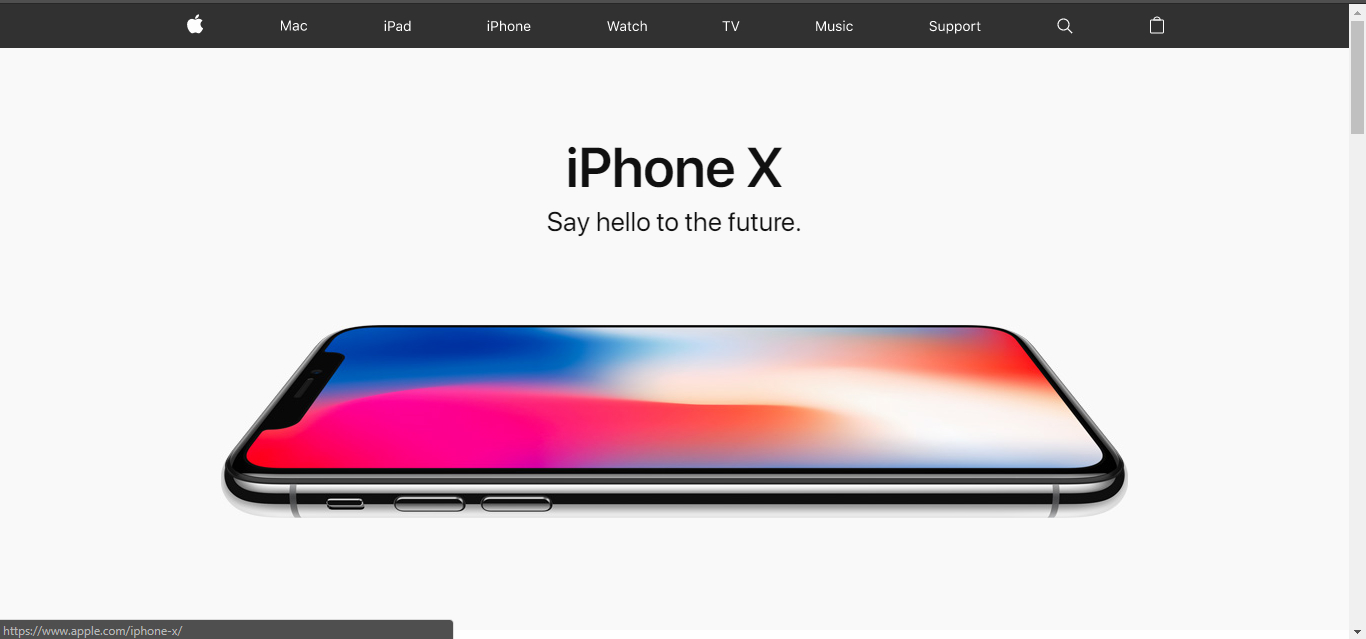
Apple.com

To keep its loyal consumer base updated regarding the upcoming releases and other products, Apple launched their very own website in 1987. However, the look and feel of the website then and now are miles apart.
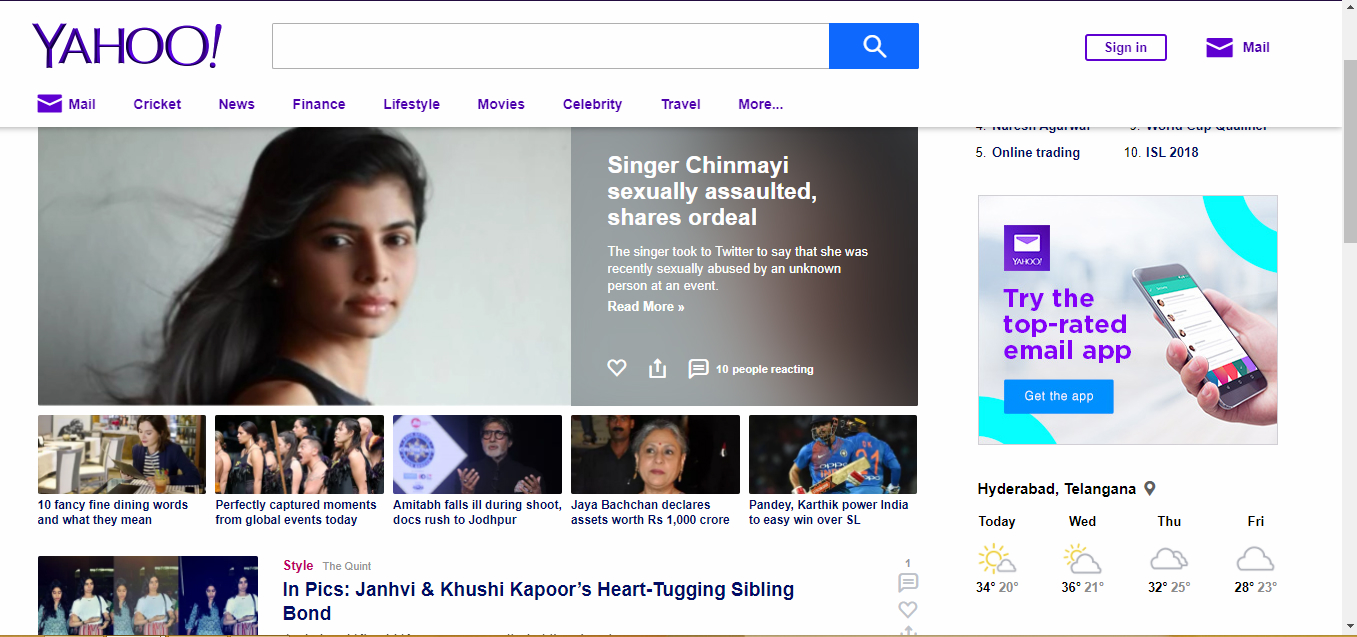
Yahoo
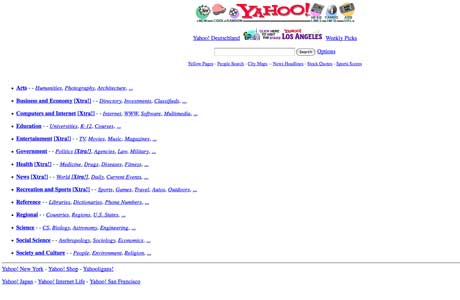
Founded by Stanford duo Jerry Yang and David Filo in 1994, Yahoo is the acronym for “Yet Another Hierarchical Officious Oracle.” Considered to be the first online navigational guide to the web, the original interface featured a simple search bar and hyperlinks to other websites but soon became a sleek, personalized news website.
eBay
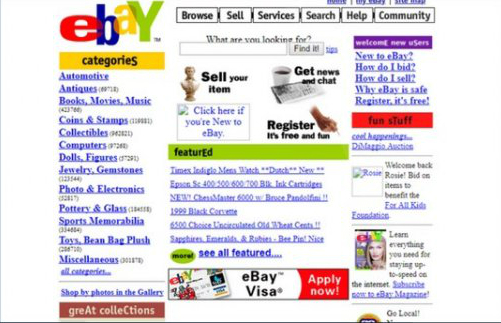
Founded by Pierre Omidyar in 1995, eBay was originally supposed to be called AuctionWeb. Today, the company has an artificial intelligence powered shopping assistant and a market capitalization of $37.48 billion.
Amazon.com
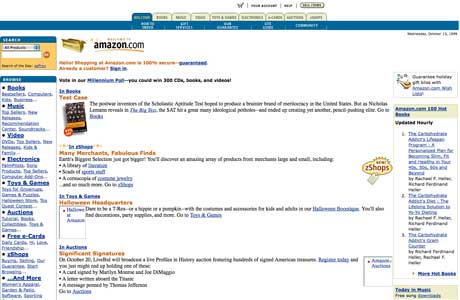
Everyone who knows the story behind Amazon knows the online retail store was first started to sell books. The ecommerce giant of today first took root in 1995, however, the company now offers deals on almost everything.
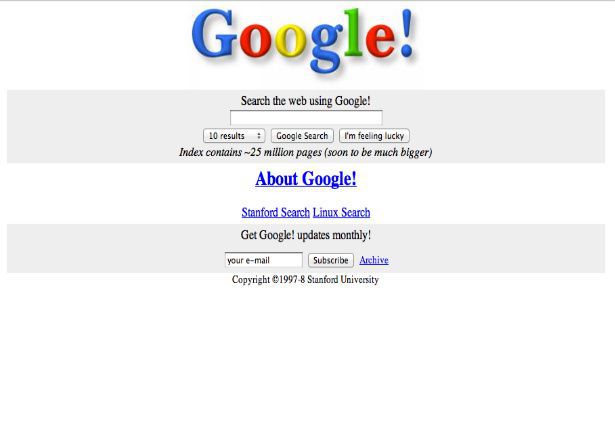
Launched in 1996, Google had a simple interface that it has continued to use to date. Google Founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin kept the user interface simply because they did not know HTML and were looking for a quick design.
Wikipedia
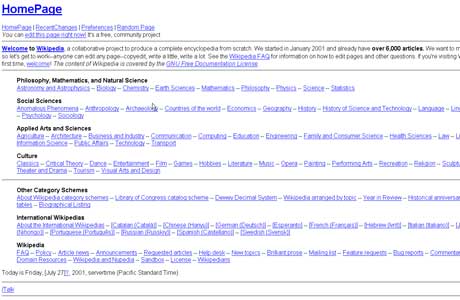
The online encyclopedia was registered by Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger on 15 January in 2001. Little has changed in the world’s fifth most popular website which receives a monthly readership of 495 million and 18 billion page views per month.
MySpace
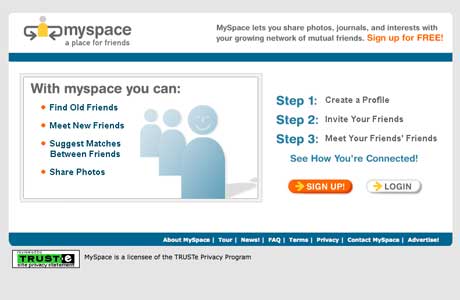
The original social networking site, MySpace had a pretty bland original design. However, the site skyrocketed in terms of popularity between 2005 and 2008 after News Corp., acquired the company.
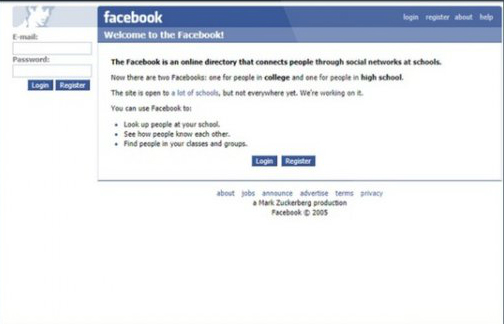
Thefacebook, as it was called in 2004, was only available to Harvard University Students. The original interface featured a man’s face on the upper left hand corner of the site which was a digitally manipulated picture of Al Pacino.
YouTube
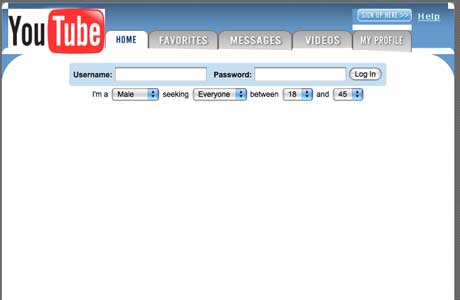
Video sharing website YouTube which shined a light on stars like Justin Bieber and hits like “Charlie bit my finger” was launched in 2005. The overall look, 12 years later still has a similar look and feel had a practically empty interface and no evidence of videos. The first video uploaded on the site was created by one of YouTube’s founders, Jawed Karim, and was titled “Me at the Zoo.”
Twitter
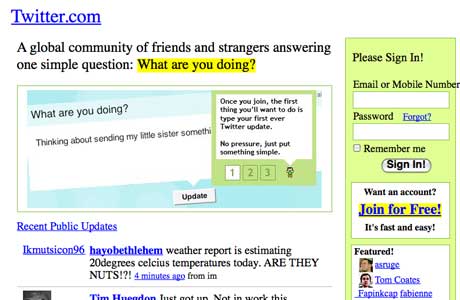
The microblogging social media website, Twitter, which gained popularity for its character limit was supposed to be called Twttr. The website had a barely recognizable design at the beginning and since then has changed their interface design at least six times.
News
Google Launches Startup Hub in Hyderabad to Boost India’s Innovation Ecosystem

Google has launched the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad, a major step in strengthening India’s dynamic startup ecosystem. This new initiative aims to empower entrepreneurs, innovators, and developers by giving them access to Google’s global expertise, mentoring programs, and advanced cloud technology. The hub reflects Google’s mission to fuel India’s digital transformation and promote innovation through the Google for Startups program.
Located in the heart of one of India’s top tech cities, the Google Startup Hub in Hyderabad will host mentorship sessions, training workshops, and networking events designed for early-stage startups. Founders will receive Google Cloud credits, expert guidance in AI, product development, and business scaling, and opportunities to collaborate with Google’s global mentors and investors. This ecosystem aims to help Indian startups grow faster and compete globally.
With Hyderabad already home to tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, the launch of the Google Startup Hub Hyderabad further cements the city’s position as a leading innovation and technology hub in India. Backed by a strong talent pool and robust infrastructure, this hub is set to become a growth engine for next-generation startups, driving innovation from India to global markets.
Technology
Jio Unveils Cloud PC Service to Bring Affordable Computing to Indian Households

- Jio Platforms has launched JioPC, a cloud-based virtual desktop service that transforms any television connected to a Jio Set Top Box into a fully functional computer.
- Users simply connect a keyboard and mouse to access a desktop-like environment, complete with web browsing, productivity tools, and educational apps—all without needing a physical PC or extra hardware.
- The service is device-agnostic and works with all consumer PC brands, making advanced computing accessible and affordable for millions across India.
JioPC is designed to support a wide range of activities, from professional work to online learning and creative projects. By leveraging Jio’s robust cloud infrastructure, users can run even compute-intensive AI applications directly from their TV screens. The platform also ensures data security and reliability, as all files and settings are safely stored in the cloud, protecting users from data loss even if their device is reset or replaced.
With JioPC, Jio aims to democratize digital access and bring high-performance computing to Indian households at a fraction of the traditional cost. The service supports popular productivity suites like LibreOffice and Microsoft Office online, and Jio is offering a free trial to encourage users to experience the benefits firsthand. This innovative move is set to reshape how people in India work, learn, and connect in the digital age.
Technology
WhatsApp Introduces Ads in Updates Tab, Keeps Chats Ad-Free

Meta has officially begun rolling out ads on WhatsApp, ending over a decade of an ad-free experience since its acquisition in 2014. The advertisements will appear only in the Updates tab, specifically within the Status feature, which lets users share photos, videos, and text updates that disappear after 24 hours—similar to Instagram Stories.
Where Ads Will Appear
- Ads will be visible exclusively in the Status section of the Updates tab, keeping personal and group chats ad-free.
- Businesses can use these ads to encourage users to interact via WhatsApp messaging.
- Meta is also introducing paid channel subscriptions and promoted channels within the Updates tab, allowing users to access premium content and discover new channels more easily.
Privacy and Targeting
Meta has emphasized that private messages, calls, and group chats will remain end-to-end encrypted and free from advertising. Ads will be personalized using limited, non-sensitive data such as location, language, followed channels, and ad interactions. Users can further manage ad preferences if they link WhatsApp to Meta’s Accounts Center.
User and Business Impact
The move marks a major shift for WhatsApp, which has long resisted advertising to preserve a clean messaging experience. While some users have criticized the change, Meta sees this as a significant opportunity to monetize WhatsApp’s 3 billion users and over 200 million businesses on the platform.
In summary, WhatsApp’s new ads will be confined to the Updates tab, ensuring personal messaging remains private and uninterrupted, while opening new monetization avenues for Meta and businesses.













Pvvaqgzq
May 26, 2025 at 3:08 am
Explore the ranked best online casinos of 2025. Compare bonuses, game selections, and trustworthiness of top platforms for secure and rewarding gameplaycasino bonus.
J88
November 6, 2025 at 2:30 pm
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
MM88
November 7, 2025 at 5:10 pm
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Kuwin
November 7, 2025 at 8:45 pm
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
站群程序
November 10, 2025 at 3:16 pm
搭载智能站群程序,自动化搭建与管理,为SEO项目提供核心驱动力。站群程序
站群程序
November 12, 2025 at 10:19 am
采用高效谷歌站群策略,快速提升网站在搜索引擎中的可见性与权重。谷歌站群
GO88
November 13, 2025 at 7:24 pm
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
iwin
November 20, 2025 at 5:21 pm
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
MM88
November 23, 2025 at 6:12 am
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
chanced casino
December 18, 2025 at 7:28 pm
chanced casino chanced casino
iwild casino code für freispiele
December 21, 2025 at 12:48 am
Ein Casino ohne Verifizierung funktioniert in der Praxis
nicht anders als ein Spielanbieter, der eine Legitimationsprüfung durchführt.
Ein Online Casino ohne Verifizierung ist ein virtueller Spielanbieter,
der auf die Identitätsprüfung der Spieler verzichtet.
Das Monsterwin Casino ist zwar erst seit 2025 am Glücksspielmarkt vertreten, kann aber trotzdem als
sicherer und seriöser Spieleanbieter empfohlen werden. Bei Spinsy kommen aber nicht nur
die Anhänger der klassischen Casinospiele zum Zuge. Online Casinos ohne Lizenz bieten eine
interessante Alternative – besonders für Spieler, die Wert auf
Flexibilität, schnelle Abwicklung und internationale Vielfalt legen. Ob
aus Deutschland, Österreich, der Schweiz oder von überall auf der Welt – Nutzer treffen online auf
eine facettenreiche Community von Casino-Fans.
Alle Glücksspiele sind für Kinder sowie Jugendliche unter 18 Jahren verboten. Wir von GambleGuys
Deutschlands diese Plattformen empfehlen, wenn Sie sich für
seriöse Casinos entscheiden und sich über die rechtlichen und lizenzrechtlichen Anforderungen zuvor im Klaren sind.
Diese Portale, sofern diese über eine gültige Lizenz einer offiziellen staatlichen Behörde
verfügen, bieten den Spielern Datenschutz, problemlose Zahlungen und die
Möglichkeit, sofort mit dem Spielen zu beginnen.
Die Freischaltung und das Durchspielen solcher Deals laufen nach dem bekannten Schema ab.
Ansonsten kannst du alle Spiele, wie Tischspiele oder Roulette und
Poker spielen. Wichtig ist, nur bei seriösen Casinos ohne Verifizierung mit gültiger Lizenz zu
spielen.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/entdecken-sie-die-ggbet-casino-mobile-app-ihr-spielerlebnis-fur-unterwegs/
Pure Casino review Australia
December 27, 2025 at 12:31 pm
I tested these on my iPhone 13 and found no lag,
even on live dealer games.Some casinos reward mobile players.
You’re most likely to win on high RTP pokies, but
luck still plays a role don’t expect to
beat the house every time.For a real casino vibe, live dealer games are unbeatable.
I came across a few AU casino with high rollers offers tailored bonuses
for players depositing $1,000 or more, often with lower wagering requirements.
Australian dollars are the most common currency at online casinos for Australian players.
Australians love online gambling, with online pokies and classic table
games amassing a huge following at casino sites.
PlayStar Casino offers a sleek and mobile-focused experience for players in New
Jersey. Hard Rock Bet Casino features a variety of thrilling online
games for new and established customers to enjoy.
The 24-hour clock starts with your first real-money wager – not your bonus spins.
Fanatics Casino stands out as perhaps the most
exciting new online casino launch in recent years.
We recommend that you always read the full terms and conditions
of a bonus on the respective casino’s website before playing.
Our goal is to provide accurate and up-to-date information so you, as
a player, can make informed decisions and find the best casinos to suit your needs.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/spirit-casino-for-australian-players/
casino sign-up bonus Australia
December 27, 2025 at 8:05 pm
The campus is located on both sides of the State Route 520 freeway, which connects it to
the cities of Bellevue and Seattle as well as the
Redmond city center. In 2009, a shopping mall called “The Commons” was completed on the campus,
bringing 1.4 million square feet (130,000 m2) of retail space, as well as restaurants, a soccer field and pub to the West Campus.
Green Building Council’s LEED Platinum certification and the International Living Future Institute’s Zero Carbon certification and has achieved Salmon Safe Certification. By adding native and adaptive vegetation, using rainwater capture for toilet flushing, and installing efficient fixtures and irrigation, the campus is projected to save more than 20 million gallons of water each year.
At the heart of the new section lies a two-acre (0.8 ha) plaza that can host events and
gatherings for both employees and the public.
Architectural portals connect the campus to the garage below, allowing employees
and visitors quick access and creating a pedestrian focus on campus.
Building 92 on the campus contains a visitor center (with
interactive exhibits) and store that are open to the public.
It is estimated to encompass over 8 million square feet (740,000 m2)
of office space and 30,000–40,000 employees.
The all-electric buildings are completely fossil-fuel
free, drawing renewable energy from off-site sources and the campus’s Thermal
Energy Center, which houses a geothermal system that provides heating and cooling for 18 buildings.
Since Microsoft established its headquarters in Redmond,
Washington, in 1986, the company’s campus has grown from four buildings to more than 100.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/viva-las-venice-a-complete-guide/
https://precisionscans.net/employer/us-online-casinos-that-accept-paypal-2025/
December 29, 2025 at 9:21 am
online casino that accepts paypal
References:
https://precisionscans.net/employer/us-online-casinos-that-accept-paypal-2025/
rank.sudapeople.tv
December 29, 2025 at 9:35 am
casino sites that accept paypal
References:
rank.sudapeople.tv
imcufideteq.gob.mx
December 30, 2025 at 1:37 pm
online blackjack paypal
References:
https://www.imcufideteq.gob.mx/employer/top-new-online-casinos-in-australia-november-2025/
jobsonly.in
December 30, 2025 at 2:29 pm
online casino paypal
References:
https://jobsonly.in/employer/best-online-casinos-in-australia-%ef%b8%8f-ranked-by-experts-2025/